the drop arm test rotator cuff|drop arm test shoulder positive : distributing This page describes the Drop Arm Test, a common test for a supraspinatus tear and/or rotator cuff tear. A video demonstration is included. Group created on April 18, 2017. See more. Tags. Entrepreneurship & Startups • Home Businesses. São Miguel Paulista, Sao Paulo, Brazil. Members · 3.3K. Activity. No new .
{plog:ftitle_list}
web11 de jan. de 2024 · Bomba Patch 2024 PPSSPP 100% Atualizado. Rumores anteriores sobre a mudança de nome do popular console de jogos PES 2022 no início da nova temporada foram confirmados. No dia 21 de julho de 2021, foi realizada uma apresentação oficial, na qual a Konami anunciou uma completa reorientação de todas as suas redes .
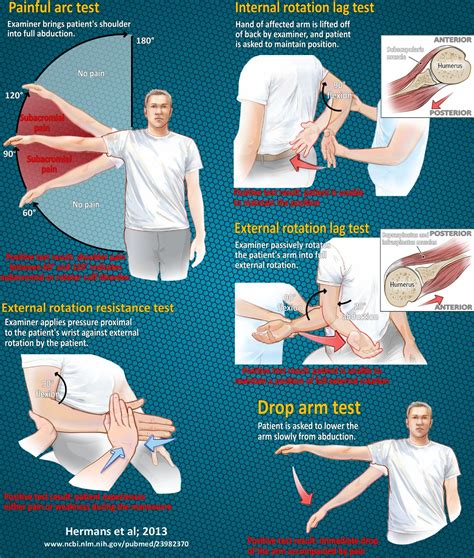
A possible rotator cuff tear can be evaluated with the drop-arm test. This test is performed by passively abducting the patient's shoulder, then observing as the patient slowly lowers.This page describes the Drop Arm Test, a common test for a supraspinatus tear and/or rotator cuff tear. A video demonstration is included.
Drop Arm Sign for Full-Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears. The Drop Arm Sign has a sensitivity of 73% and a specificity of 77% in the diagnosis of full-thickness tears of the Supraspinatus and Infraspinatus tendons according to a study done by . How it’s performed: A doctor will raise your arm to your side and bend your elbow to 90 degrees. You will then externally rotate your arm as the doctor resists. What it tests for: Damage to the. This is a really great test for you to use with your patients who you suspect may have injured their Rotator Cuff, and in particular, may have suffered a Rot. summary. Rotator cuff tears are a very common source of shoulder pain and decreased motion that can occur due to both traumatic injuries in young patients as well as degenerative disease in the elderly patient. .
shoulder test for rotator cuff
rotator cuff tear physical exam
A positive drop arm test increased the likelihood of rotator cuff disease (one study with 104 patients and 104 shoulders; positive likelihood ratio = 3.3; 95% CI, 1.0 to 11).
The drop arm test can help determine the integrity of the rotator cuff musculature, specifically supraspinatus. A positive test is the inability of the individual to lower their arm to their side under control from 90 degrees of .The cluster for a full thickness rotator cuff tear includes 1. the Drop-arm sign, 2. the painful arc sign, and 3. infraspinatus manual muscle test. If all three tests are positive, the +LR is 15.6 . (Note is 3/3 are positive and the patient is greater .
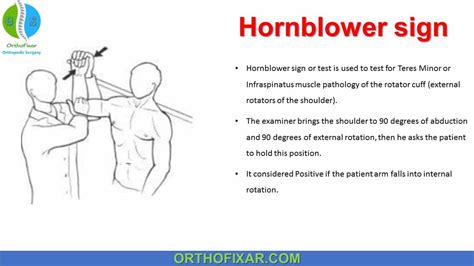
positive hornblower's sign
To test the presence of a shoulder full-thickness rotator cuff tear using the Drop-Arm Sign, Painful Arc Sign, and the Infraspinatus Muscle Test. Evidence [ edit | edit source ] Based on the Park et al [1] study, the combination of the . A positive drop arm test increased the likelihood of rotator cuff disease (one study with 104 patients and 104 shoulders; positive likelihood ratio = 3.3; 95% CI, 1.0 to 11).As Prices Drop, Point-of-Care Ultrasound May Spark Evolution of Physical Exam . The supraspinatus tendon is the most frequently injured tendon of the rotator cuff. To test for integrity of the supraspinatus we can ask the patient to abduct both arms to 90° and then to bring them anteriorly with a 30° forward flexion. . If the patient .The drop arm test is used to assess for full thickness rotator cuff tears, particularly of the supraspinatus. This can be useful when diagnosing sub-acromial pain syndrome (shoulder impingment) or to differentiate between shoulder and rotator cuff pathologies. The drop arm test may be more accurate when used in a battery of tests such as:
positive drop arm test
Codman's test is typically used in the assessment of a suspected rotator cuff tear. This test is also commonly referred to as the drop-arm test or sign. Technique [edit | edit source] The therapist passively raises the patient's arm to 90 degrees of abduction. The patient then lowers the arm back to neutral with the palm down.Rotator cuff tear (Supraspinatus) Drop Arm Test / Codman's Test; Empty Can Test; Full Can Test; Rotator cuff tear (Supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles) and shoulder impingement External Rotation Lag Sign; Rotator cuff tear (Subscapularis) Internal Rotation Lag Sign; Lift-Off Test (Gerber’s Test)The Drop Arm test is used to help identify rotator cuff pathology, specifically supraspinatus and infraspinatus tears. How to Perform Drop Arm Test. Position of Patient: Patient is sitting or standing with arm relaxed at side. Performance: The examiner passively places the patient’s arm into abduction of 90 degrees. The patient is instructed .Two such commonly employed shoulder tests to diagnose a torn rotator cuff is the Drop Arm Test and the Hornblower Test. More than pain in the shoulder joint, it is significant weakness on the affected side that could be a strong indicator of rotator cuff tears. Along with these tests imaging tests like an MRI could help confirm the diagnosis.

Drop arm test. The drop arm test is used to assess for rotator cuff tears, particularly of the supraspinatus. Interpretation. Drop arm test is negative if the patient is able to control the lowering of the arm slowly and without pain. Enroll in our online course: http://bit.ly/PTMSK DOWNLOAD OUR APP:📱 iPhone/iPad: https://goo.gl/eUuF7w🤖 Android: https://goo.gl/3NKzJX GET OUR ASSESSMENT B. Rotator Cuff. Supraspinatus (SS) Jobe’s test: Positive test is pain/weakness with resisted downward pressure while the patient’s shoulder is at 90 degrees of forward flexion and abduction in the scapular plane with the thumb pointing toward the floor. Drop arm test: The patient’s shoulder is brought into a position of 90 degrees of .
Purpose [edit | edit source]. This is a shoulder special test which is meant to assess the integrity, and tears, of the supraspinatus (SSP) and infraspinatus muscles (muscles which collectively contribute to the rotator cuff complex). This test can also be used for the clinical examination of a shoulder impingement syndrome (SIS).. Another name for this test is the Infraspinatus . Drop Arm Test. This simple test assesses the possibility of a rotator cuff tear. During the test, the patient (either sitting or standing) holds their arm straight out at a 90 degree angle, then slowly lowers the arm down to their side. The provider is looking for the patient’s ability to raise and lower the arm in a controlled manner.
positive drop arm sign
Purpose: Clinical diagnosis of posterosuperior rotator cuff tears remains uncertain due to a lack of evidence-based consensus. This review aimed to compare the diagnostic accuracy of commonly used clinical tests for posterosuperior rotator cuff tears. Methods: The authors conducted an electronic literature search using Medline, Embase and the Cochrane .
pf水分計
Rotator cuff tears are a very common source of shoulder pain and decreased motion that can occur due to both traumatic injuries in young patients as well as degenerative disease in the elderly patient. . Drop arm . A rotator cuff tear is an injury to your rotator cuff that can cause shoulder pain and the inability to use your arm. Your rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons in your shoulder. They help you lift and move your arms away from your body. Your rotator cuff keeps the ball of your upper arm bone in the shoulder blade socket.
Rotator Cuff Tests. Supraspinatus Test (+ LR 3.2) Abduct arm to 90', forward flex it 30' with thumb down ("empty beer can position") . Drop arm test Patient is unable to hold or smoothly lower an extended arm at 90' of shoulder abduction with out dropping it; Differential Diagnosis
влагомер
Your rotator cuff is a group of four muscles that connects your shoulder blade to your upper arm bone (humerus).You use your rotator cuff to raise your arm overhead and to rotate your arm toward and away from your body. The rotator cuff sits in a small space between your humerus and the acromion (the upper part of your shoulder blade).Home tests including the Drop Arm Test, Apley Scratch Test, and Lift-off Test can help identify potential rotator cuff injuries, but should be complemented by professional medical evaluation for accurate diagnosis. . an essential component of your rotator cuff. This test is particularly useful because the subscapularis muscle plays a crucial . Negative Test: The patient can smoothly and slowly lower the arm without difficulty, indicating the absence of significant rotator cuff pathology.; How the Drop Arm Test Helps in Diagnosing Rotator Cuff Tears? The drop arm test serves as a valuable screening tool for detecting rotator cuff tears, particularly involving the supraspinatus tendon.A positive test .
A supraspinatus tear is a tear or rupture of the tendon of the supraspinatus muscle. The supraspinatus is part of the rotator cuff of the shoulder. Most of the time, it is accompanied by another rotator cuff muscle tear.This can occur due to trauma or repeated micro-trauma and present as a partial or full-thickness tear. Quite often, the tear occurs in the tendon or as an .
- Drop arm test - External rotation testing of shoulder - Passive Painful Arc Neer Test - Scapular assistance maneuver . - Painful arc sign for rotator cuff pathology - Jobe test of supraspinatus strength - External rotation test - Gerbers test - . The drop arm sign is often used to diagnose a rotator cuff tear. The examiner brings the arm to 90 degrees of abduction and instructs the patient to maintai. A positive drop arm test indicates a potential rotator cuff tear or injury. If the patient is unable to maintain control of their arm during the descent, experiences pain, or has weakness in the affected shoulder, it suggests a significant rotator cuff problem. Further diagnostic imaging, such as an MRI, may be needed to confirm the diagnosis.This test may be combined as a cluster with the Drop-Arm Sign and the Painful Arc Sign to test for the presence of a full-thickness rotator cuff tear. If all three tests report positive results, then the positive likelihood ratio is 15.6 and if all three tests are negative, the negative likelihood ratio is .
The drop arm test is designed to determine a patient's ability to sustain humeral joint motion through eccentric contraction as the arm is taken through the full motion of abduction to adduction. It will determine if the patient has an underlying rotator cuff dysfunction. [1] Procedure
влагомер древесины
влагомер зерна
WEBVenda bolo fake stumble guy. Bolo Fake Stumble Guys feitas especialmente para você. Mais de 131 produtos exclusivos. A maior variedade de produtos e com diversas opções de pagamento..
the drop arm test rotator cuff|drop arm test shoulder positive